
一种多孔TOC模型,用于球体形成、长期原位培养和药物评估。
Introduction
第一个被FDA批准的纳米药物,即阿霉素脂质体(Liposome-based Doxil)的成功,引发了人们对开发新的癌症治疗纳米药物的巨大兴趣。然而,尽管在过去十年中付出了很多努力,但只有少数纳米药物被批准用于人类。
- 挑战之一是难以以简单且可重现的方式生产具有精确控制特性的纳米药物,特别是具有多种功能如靶向、成像和可控释放的纳米药物。
- 另一个挑战是缺乏快速、可靠且经济高效的评估模型以快速筛选大型文库中具有特定性质的纳米药物,例如粒径、电荷、表面性质、配体密度和机械性质等。
本研究中,作者设计和制造了多孔TOC模型,用于球体形成、长期原位培养和药物评估。设备中嵌入了不同尺寸的半球孔,用于制造不同尺寸的肿瘤球,从而可以同时评估多种药物制剂在不同尺寸的肿瘤球上的药效。此外四种不同的脂质体制剂,包括聚乙二醇化脂质体(PEG-Lip)、叶酸修饰脂质体(FA-Lip)、细胞穿透肽TAT修饰脂质体(TAT-Lip)以及叶酸和TAT共修饰脂质体(FA-TAT-Lip)被用来评估它们的肿瘤靶向性和抗癌功效。
TOC Design and Simulation
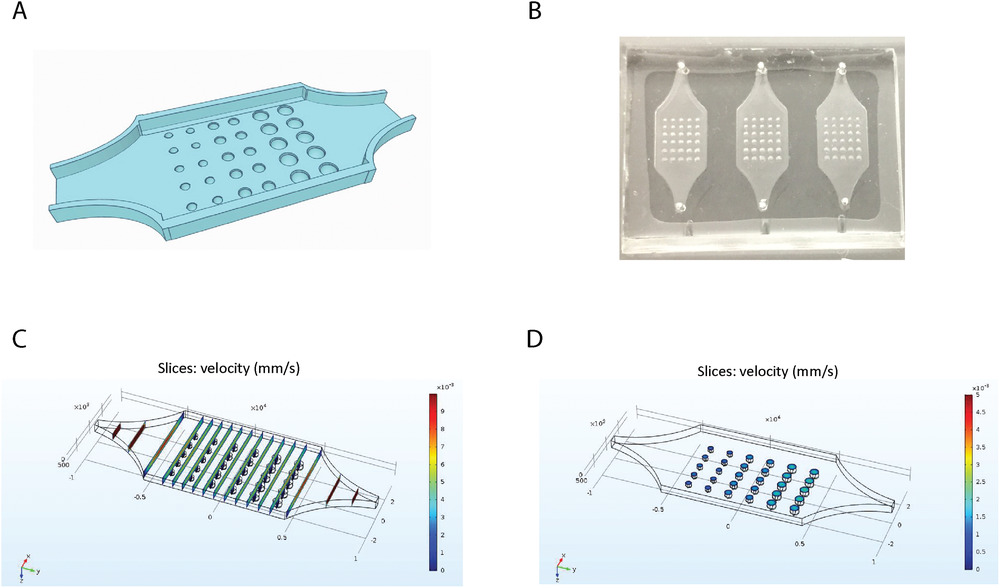
- (A)TOC装置设计示意图。流体腔中嵌入了30个半球孔,半径分别为200、250和300 µm。
- (B)使用3D打印TOC模具,并使用标准的软光刻技术制作TOC芯片。其长度、宽度和高度分别为1 cm、0.7 cm和600 µm。
- (C)装置中不同垂直截面的速度表明,半球孔上方的速度是相似的。
- (D)无论大小如何,半球孔内部的速度均无显著差异。
Evaluation of Multifunctional Liposomes’ Tumor Targeting Using TOC Model and Animal Model
使用TOC模型和动物研究,对四种不同类型的脂质体(PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip)的肿瘤积累进行归一化处理。
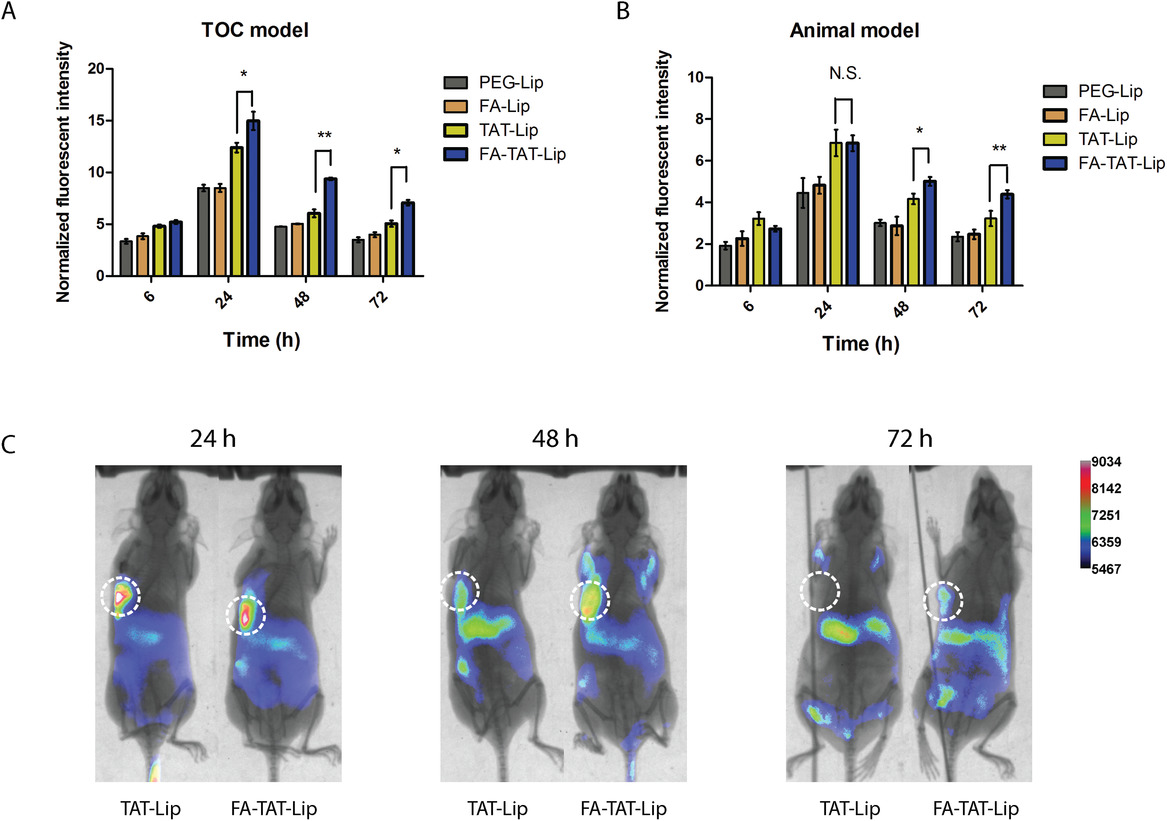
- (A)在TOC装置中时间推移的肿瘤吸收效率。将含有DiI标记的脂质体的培养基以1 µL min-1的流速灌注TOC装置24 h,然后再用新鲜培养基替换48 h。
- (B)先前的研究中的单剂量DiR标记脂质体在动物模型中随时间推移的肿瘤吸收效率。
- (C)系统性施用DiR加载的TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip后,在不同时间点SKOV3肿瘤的小鼠的体内全动物荧光图像。虚线圆圈指示肿瘤的位置。
Cytotoxicity and Treatment Efficacy Study Using the TOC Model in Comparison with 2D Monolayer Cell Culture and 3D Tumor Spheroid Models
Table 1. The compositions of PTX‐loaded PEG‐Lip, FA‐Lip, TAT‐Lip, and FA‐TAT‐Lip
| Liposome | DMPC [mol%] | CHO [mol%] | PEG [mol%] | FA [mol%] | TAT [mol%] | PTX [w/w] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG‐Lip | 55 | 40 | 5 | – | – | 5% |
| FA‐Lip | 55 | 40 | 4 | 1 | – | 5% |
| TAT‐Lip | 55 | 40 | 4 | – | 1 | 5% |
| FA‐TAT‐Lip | 55 | 40 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5% |
- DMPC: 1,2‐Dimyristoyl‐sn‐glycero‐3‐phosphocholine,二肉豆蔻酰磷脂酰胆碱。
- CHO: cholesterol,胆固醇。
- PEG: 1,2‐distearoyl‐sn‐glycero‐3‐phosphoethanolamine‐N‐[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)‐2000],聚乙二醇。
Table 2. Particle size, polydispersity (PDI) and encapsulation efficiency (EE) of the PTX‐loaded liposome formulations (n = 3, mean ± SD)
| Liposome | Size [nm] | PDI | EE [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG‐Lip | 72 ± 4 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 91 ± 2 |
| FA‐Lip | 73 ± 3 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 91 ± 1 |
| TAT‐Lip | 92 ± 2 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 92 ± 2 |
| FA‐TAT‐Lip | 88 ± 2 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 92 ± 2 |
- PDI: polydispersity index,多分散指数。
- EE: encapsulation efficiency,包封率。
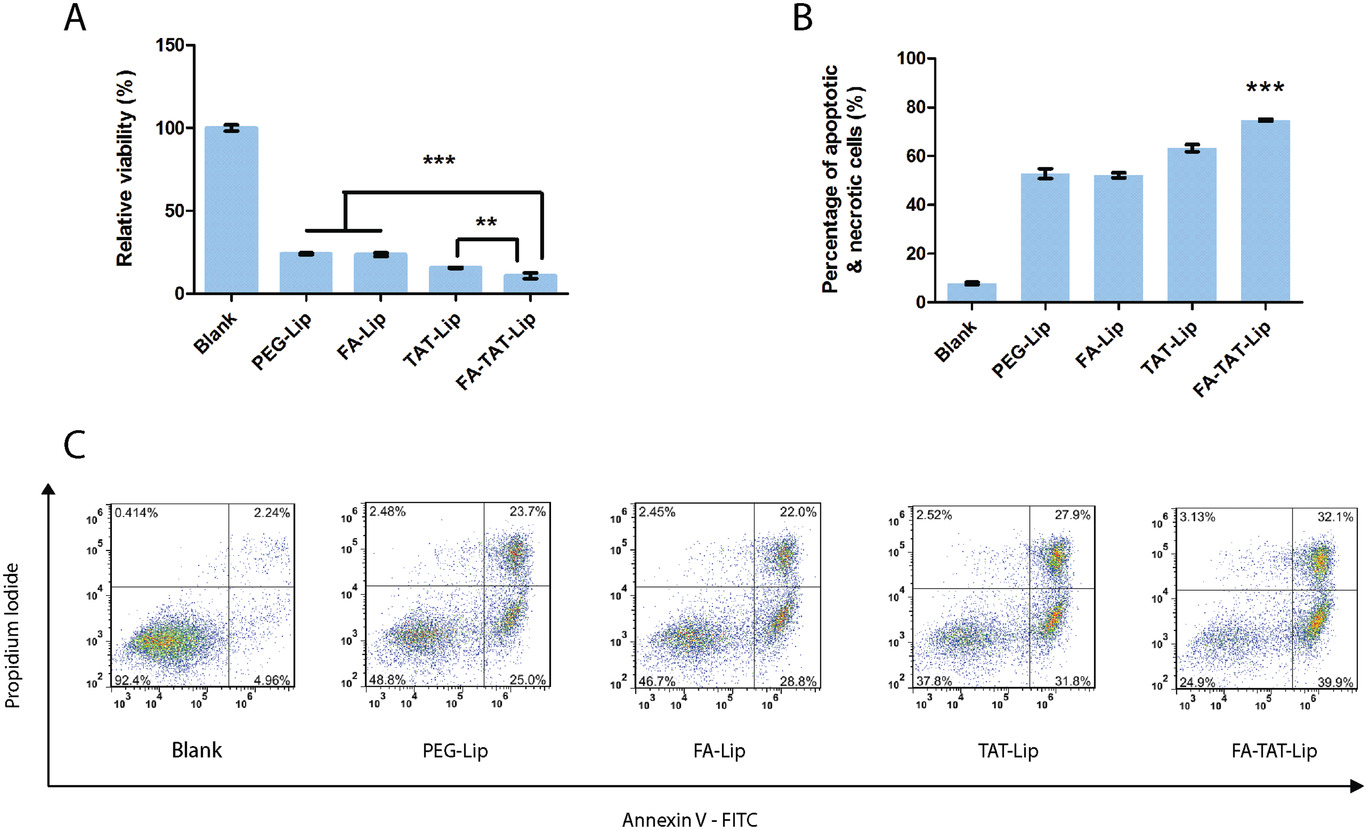
- (A)通过APH试验检测0.1 µg mL−1PTX装载的PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip的细胞毒性。
- (B)凋亡和坏死细胞百分比。
- (C)用1.5 µg mL−1PTX装载的PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip处理SKOV3细胞24 h的散点图。

- (A)通过APH试验检测0.1 µg mL−1PTX装载的PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip的细胞毒性。
- (B)PTX装载的PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip处理72 h的肿瘤球生长曲线。向上箭头(第0天)表示添加脂质体药物的时间;向下箭头(第3天)表示逐渐移除药物的开始日期。每48 h替换总培养基的50%。
- (C)药物孵化时期对应的肿瘤球形态。第0天,加入药物;第3天,药物逐渐移除。每48 h替换总培养基的50%。
APH:acid phosphatase,酸性磷酸酶。
SKOV3:人卵巢癌细胞系。
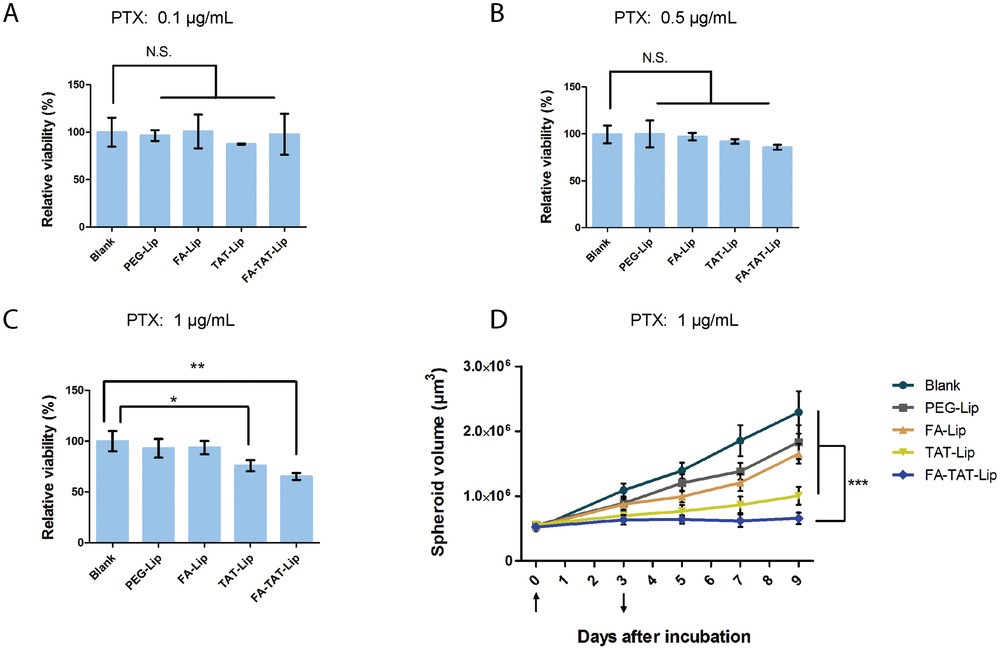
- (A-C)利用TOC模型进行细胞毒性及肿瘤抑制疗效研究。APH试验测定分别使用0.1µg mL−1(A)、0.5µg mL−1(B)和1µg mL−1(C)的PTX装载PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT- Lip的细胞毒性。流速是1 µL min−1,孵育时间为72 h。
- (D)最大半球孔中,PTX装载的PEG-Lip、FA-Lip、TAT-Lip和FA-TAT-Lip处理72 h的肿瘤球生长曲线。PTX浓度为1 µg mL−1,流速是1 µL min−1。向上箭头(第0天)表示药物装载培养基的灌注时间;向下箭头(第3天)表示无药物的新鲜培养基的灌注时间。每48 h替换总培养基的50%。
Effect of Flow Rates on Treatment Efficacy

- (A)不同流速下PTX装载的FA-TAT-Lip灌注72 h后,通过APH试验测定SKOV3肿瘤球的存活率。
- (B)最大半球孔中,不同流速下,PTX装载的FA-TAT-Lip处理72 h的肿瘤球生长曲线。PTX浓度为1 µg mL−1。向上箭头(第0天)表示药物装载培养基的灌注时间;向下箭头(第3天)表示无药物的新鲜培养基的灌注时间。
- (C)通过流式细胞术(FACS)测量的不同流速下的总脂质体摄取效率。
Effect of Tumor Spheroid Sizes on Treatment Efficacy
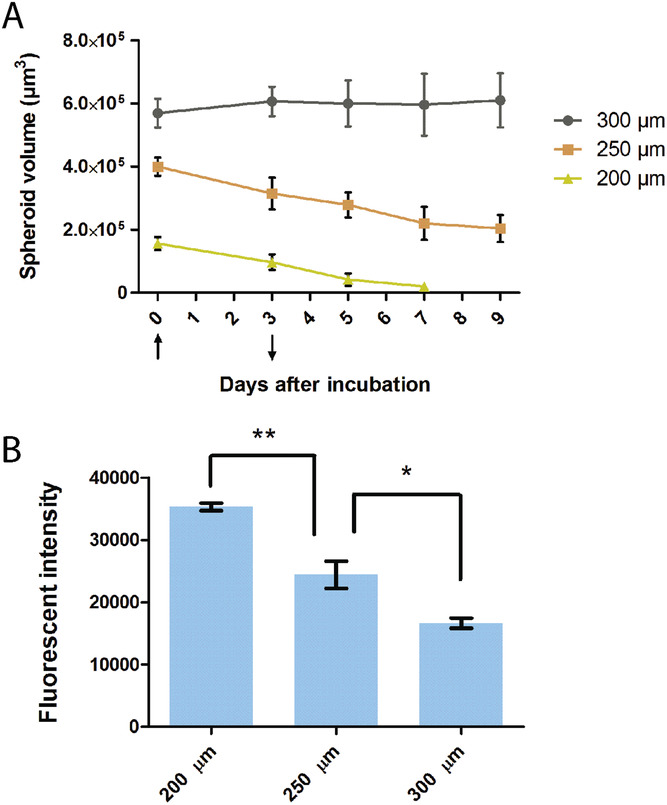
- (A)PTX装载的FA-TAT-Lip灌注后,不同大小的半球孔(200、250、300 µm)内肿瘤球的生长曲线。PTX的浓度为1 µg mL−1,流速为1 µL min−1。向上箭头(第0天)表示药物装载培养基的灌注时间;向下箭头(第3天)表示无药物的新鲜培养基的灌注时间。
- (B)采用流式细胞术(FACS)测量不同尺寸半球孔中肿瘤球的整体吸收效率。
Conclusion
设计并制造了一个微流控TOC装置,用于评估基于脂质体的纳米医学药物的抗癌效果。这个TOC模型允许在同一个装置中进行肿瘤细胞的装载、肿瘤球形成、长期培养和药物评估。此外,利用这个TOC模型,在微流控室中嵌入了三组不同大小的半球形孔,可以对不同大小的肿瘤球体进行药效评估。
与2D细胞和3D肿瘤球模型相比,这个TOC模型提供了更接近于表示体内脂质体肿瘤的积累和治疗效果。使用这个TOC模型,观察到较低的流速和较小的肿瘤球状体尺寸导致了治疗效果的改善。这项工作表明,TOC设备可以作为一个有价值的体外模型,用于快速和可靠的药物评估。
Reference
Ran R, Wang H-F, Hou F, et al. A Microfluidic Tumor-on-a-Chip for Assessing Multifunctional Liposomes’ Tumor Targeting and Anticancer Efficacy[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(8): 1900015.



